Supported products
Supported products
Required Scopes
Required Scopes
Create a custom object
To create a custom object, you’ll first need to define the object schema. The schema includes the object name, properties, and associations to other CRM objects. You can find the full schema request details in the Object schema tab at the top of this article. You can also view a sample request in the example walkthrough below. To create the custom object schema, make aPOST request to crm/v3/schemas. In the request body, include definitions for your object schema, including its name, properties, and associations.
When naming your custom object, keep the following in mind:
- Once you create an object, its name and label cannot be changed.
- The name can only contain letters, numbers, and underscores.
- The first character of the name must be a letter.
- Long labels may be cut off in certain parts of the product.
Properties
The properties you define in the request body will be used to store information on individual custom object records. You’ll use your defined properties to populate the following property-based fields:- requiredProperties: the properties that are required when creating a new custom object record.
- searchableProperties: the properties that are indexed for searching in HubSpot.
- primaryDisplayProperty: the property used for naming individual custom object records.
- secondaryDisplayProperties: the properties that appear on individual records under the primaryDisplayProperty.
-
The first property listed in
secondaryDisplayPropertieswill be also added as a fourth filter on the object index page if it’s one of the following property types:stringnumberenumerationbooleandatetime
- To remove a display property from the UI, you’ll need to first delete the property, then recreate it.
type is set to string, and the fieldType is set to text. Below are the values you can use to create different types of properties.
type | Description | Valid fieldType values |
|---|---|---|
enumeration | A string representing a set of options, separated by semicolons. | booleancheckbox, checkbox, radio, select |
date | An ISO 8601 formatted value representing a specific day, month, and year. | date |
dateTime | An ISO 8601 formatted value representing a specific day, month, year and time of day. The HubSpot app will not display the time of day. | date |
string | A plain text strings, limited to 65,536 characters. | file, text, textarea |
number | A number value containing numeric digits and at most one decimal. | number |
fieldType | Description |
|---|---|
booleancheckbox | An input that will allow users to select one of either Yes or No. When used in a form, it will be displayed as a single checkbox. |
checkbox | A list of checkboxes that will allow a user to select multiple options from a set of options allowed for the property. |
date | A date value, displayed as a date picker. |
file | Allows for a file to be uploaded to a form. Stored and displayed as a URL link to the file. |
number | A string of numerals or numbers written in decimal or scientific notation. |
radio | An input that will allow users to select one of a set of options allowed for the property. When used in a form, this will be displayed as a set of radio buttons. |
select | A dropdown input that will allow users to select one of a set of options allowed for the property. |
text | A plain text string, displayed in a single line text input. |
textarea | A plain text string, displayed as a multi-line text input. |
Associations
HubSpot will automatically associate a custom object with the emails, meetings, notes, tasks, calls, and conversations objects. You can further associate your custom object with other standard HubSpot objects or other custom objects. When creating associations through the create schema request, identify standard objects using their name and custom objects using theirobjectTypeId value. For example:
Retrieve existing custom objects
To retrieve all custom objects, make aGET request to /crm/v3/schemas.
To retrieve a specific custom object, make a GET request to one of the following:
/crm/v3/schemas/{fullyQualifiedName}/crm/v3/schemas/{objectTypeId}
fullyQualifiedName (formatted as p{Hub_ID}_{object_name}) and objectTypeId in its schema. You can find your account’s Hub ID using the account information API.
For example, for an account with a Hub ID of 1234, to retrieve an object named lender with the objectTypeId value 2-7282133, your request URL could look like either of the following:
/crm/v3/schemas/p1234_lender/crm/v3/schemas/2-7282133
Retrieve custom object records
You can also retrieve a custom object’s records.- To retrieve a specific record by its record ID value, make a
GETrequest tocrm/v3/objects/{objectType}/{recordId}.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
properties | A comma separated list of the properties to be returned in the response. If the requested custom object record doesn’t have a value for a property, it will not appear in the response. |
propertiesWithHistory | A comma separated list of the current and historical properties to be returned in the response. If the requested custom object record doesn’t have a value for a property, it will not appear in the response. |
associations | A comma separated list of objects to retrieve associated IDs for. Any specified associations that don’t exist will not be returned in the response. Learn more about the associations API. |
- To retrieve multiple records, make a
POSTrequest tocrm/v3/objects/{objectType}/batch/read. The batch endpoint cannot retrieve associations. Learn how to batch read associations with the associations API.
hs_object_id), or by a custom unique identifier property. By default, the id values in the request refer to the record ID, so the idProperty parameter is not required when retrieving by record ID. To use a custom unique value property, you must include the idProperty parameter.
For example, to retrieve a batch of custom object records, your request could look like either of the following:
Update existing custom objects
To update an object’s schema, make aPATCH request to https://api.hubapi.com/crm/v3/schemas/{objectTypeId}.
Once your custom object is defined:
- The object’s name and labels (singular and plural) cannot be changed.
- The
requiredProperties,searchableProperties,primaryDisplayProperty, andsecondaryDisplayPropertiescan be changed by updating the object’s schema. To set a new property as a required, searchable, or display property, you need to create the property prior to updating the schema. - You can create and edit custom object properties either in HubSpot or via the properties API.
Update associations
To add other object associations to your custom object, make aPOST request to /crm/v3/schemas/_{objectTypeId}_/associations.
You can only associate your custom object with standard HubSpot objects (e.g. contact, company, deal, or ticket) or other custom objects. In the toObjectTypeId field, identify custom objects by their objectTypeId value and standard objects by their name. For example:
Delete a custom object
You can only delete a custom object after all object instances of that type are deleted. To delete a custom object, make aDELETE request to /crm/v3/schemas/{objectType}.
If you need to create a new custom object with the same name as the deleted object, you must hard delete the schema by making a DELETE request to /crm/v3/schemas/{objectType}?archived=true. You can only delete a custom object type after all object instances of that type, associations, and custom object properties are deleted.
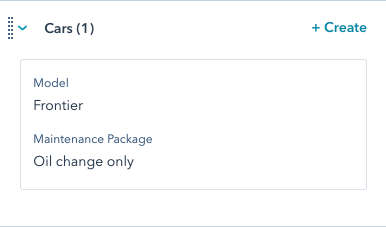
Custom object example
The following is a walkthrough of creating an example custom object. For full details of the requests shown, view the Object Definition tab at the top of the article. This walkthrough covers:- creating a custom object schema.
- creating a custom object record.
- associating a custom object record with a HubSpot contact.
- creating a new association definition between the custom object and HubSpot ticket.
- creating a new property definition.
-
updating the object schema (i.e.
secondaryDisplayProperties) with the new property.
Create the object schema
CarSpot needs to create an object schema that can represent the following attributes as properties:- Condition (new or used): enumeration
- Date received at dealership: date
- Year: number
- Make: string
- Model: string
- VIN: string (unique value)
- Color: string
- Mileage: number
- Price: number
- Notes: string
POST request to /crm/v3/schemas with the following request body:
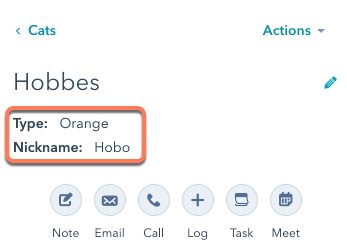
Create a custom object record
With the custom object created, CarSpot can now create records on the object for each car in their inventory. They’ll create their first car by making aPOST request to /crm/v3/objects/2-3465404 with the following request body:
id value to later associate the car with an existing contact.
Associate the custom object record to another record
You can use the ID of the new car record (181308) and the ID of another record to associate a custom object record with a record of another object.
To create an association, make a PUT request to /crm/v3/objects/{objectType}/{objectId}/associations/{toObjectType}/{toObjectId}/{associationType}. If the object relationship is already defined, to determine the associationType value, make a GET request to crm/v3/schemas/{objectType}.
For example, with the contact ID 51 and the association type 75, CarSpot can associate the car record with a contact. Using the above IDs, the request URL will be constructed as follows:
https://api.hubspot.com/crm/v3/objects/2-3465404/181308/associations/contacts/51/75
Define a new association
CarSpot now wants to start tracking post-sale services for their cars. To do so, they’ll use HubSpot tickets to log any maintenance performed. To allow associations between cars and tickets, they’ll create a new association by making aPOST request to /crm/v3/schemas/2-3465404/associations with the following request body:
When creating a new association between two custom objects, specify the custom objects by their objectTypeId in the toObjectTypeId field. For standard objects, you can identify them by name or use the following values:
- Contact: 0-1
- Company: 0-2
- Deal: 0-3
- Ticket: 0-5
Define a new property
As they continue to track maintenance, CarSpot sees an opportunity to bundle maintenance services into packages. To track these maintenance packages on individual car records, they’ll create a new enumeration property containing the available packages. To define a new property, they’ll make aPOST request to /crm/v3/properties/2-3465404 with the following request body:
secondaryDisplayProperties by making a PATCH request to /crm/v3/schemas/2-3465404 with the following request body: