Functions in HubL are similar to filters in that they accept parameters and generate a value. However, not all functions need to be applied to an initial template value, and instead they interact with other areas of your HubSpot environment.
If you maintain an older website, you may also want to check out the list of deprecated HubL functions.
Below, learn more about each HubL function and its syntax.
append
Adds a single item to the end of a list.
{% set numbers_under_5 = [1,2,3] %}
{% do numbers_under_5.append(4) %}
{{numbers_under_5}}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
item | Any | Item to be appended to the list. |
blog_all_posts_url
The blog_all_posts_url function returns a full URL to the listing page for all blog posts for the specified blog.
The example below shows how this function can be used as an anchor’s href.
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_all_posts_url("default") }}">All Marketing blog posts</a>
<a href="http://www.hubspot.com/marketing/all">All Marketing blog posts</a>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use. The blog id is returned by the module blog field. |
blog_author_url
The blog_author_url function returns a full URL to the specified blog author’s listing page.
The example below shows how this function can be used as an anchor’s href. This can be combined with blog_authors as shown in that function’s examples.
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_author_url("default", "brian-halligan") }}">Brian Halligan</a>
<a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/author/brian-halligan"
>Brian Halligan</a
>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog the author’s listing page exists in. You can specify a blog by ID or use "default" to select the default blog. The blog ID is returned by the module blog field. |
author_slug | String or HubL Var | Specifies which author to link to. Can use either content.blog_post_author.slug or a lowercase hyphenated name. Example: "jane-doe". |
blog_authors
The blog_authors function returns a sequence of blog author objects for the specified blog, sorted by slug ascending. This sequence can be stored in a variable and iterated through to create custom author post filters.
The number of live posts by each author can be accessed with author.live_posts.
Please note:This function has a limit of 250 authors. This function also has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
{{ blog_authors("default", 250) }}
{% set my_authors = blog_authors("default", 250) %}
<ul>
{% for author in my_authors %}
<li><a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_author_url(group.id, author.slug) }}">{{ author }}</a></li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
[ Tim Cramblin, Sam Duvet, Sheila Portnadi, Rhonda Devereux]
<ul>
<li><a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/author/tim-cramblin">Tim Cramblin</a></li>
<li><a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/author/sam-duvet">Sam Duvet</a></li>
<li><a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/author/sheila-portnadi">Sheila Portnadi</a></li>
<li><a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/author/rhonda-devereux">Rhonda Devereux</a></li>
</ul>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use, either a specific blog by its ID or the default blog by "default". The blog ID is returned by the module blog field. |
limit | Integer | Sets the limit on the number of authors fetched. |
blog_by_id
The blog_by_id function returns a blog by ID. The below example code shows this function in use to generate a hyperlinked list item.
Please note:This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
{% set my_blog = blog_by_id(47104297) %}
<ul>
<li>
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ my_blog.absolute_url }}">{{my_blog.html_title}}</a>
</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="http://blog.bikinginearnest.com/outdoors"
>Outdoor biking for the earnest</a
>
</li>
</ul>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use, either a specific blog by its ID or the default blog by "default". The blog ID is returned by the module blog field. |
blog_page_link
The blog_page_link function generates the URL of a paginated view of your blog listing. The function takes a numeric parameter, which allows you to generate links for current, next, previous, or a specific page. This function is generally used in the href attribute of pagination anchor tags and must be used on your blog listing template.
The examples below show this function in use as an anchor href. The first example outputs the current page. The second example takes the number 7 parameter to specify the seventh page. The third example uses the next_page_num variable to generate a link that is relative to the current page number (you can also use the last_page_num variable for the previous page). The final example uses the current_page_num variable and a + operator to create a link that is 4 greater than the current page.
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_page_link(current_page_num) }}">Current page</a>
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_page_link(7) }}">Page 7</a>
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_page_link(next_page_num) }}">Next</a>
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_page_link(current_page_num + 4) }}">Page Plus 4</a>
<a href="http://designers.hubspot.com/blog/page/1">Page 1</a>
<a href="http://designers.hubspot.com/blog/page/7">Page 7</a>
<a href="http://designers.hubspot.com/blog/page/2">Next</a>
<a href="http://designers.hubspot.com/blog/page/5">Page Plus 4</a>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
page | Number or HubL variable | Page number used to generate URL or HubL variable for page number. |
blog_popular_posts
This function renders a set number of popular posts into a sequence. The sequence can then be saved into a variable and iterated through with a for loop, creating a custom post listing of your most popular posts.
Results from this function are cached for six hours. To retrieve blog posts using HubL in a way that avoids caching, you may want to use blog_recent_tag_posts instead.
In the example code below, the first line shows how the function returns a sequence. The sequence is saved as a variable which is then used in a for loop. Any blog post variables should use the name of the individual loop item rather than content.. In the example, pop_post.name is used. This technique can be used on blog templates and website pages.
Please note:This function has a limit of 200 posts. This function also has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
{% set pop_posts = blog_popular_posts("default", 5, ["marketing-tips", "sales-tips"], "popular_past_month", "AND") %}
{% for pop_post in pop_posts %}
<div class="post-title">{{ pop_post.name }}</div>
{% endfor %}
[Popular post title 1, Popular post title 2, Popular post title 3, Popular post
title 4, Popular post title 5]
<div class="post-title">Popular post title 1</div>
<div class="post-title">Popular post title 2</div>
<div class="post-title">Popular post title 3</div>
<div class="post-title">Popular post title 4</div>
<div class="post-title">Popular post title 5</div>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use, either a specific blog by its ID or the default blog by "default". |
limit | Integer | Specifies the number of posts to add to the sequence up to a limit of 200. If not specified, defaults to 10. |
tag_slug | Array | Optional list of tags to filter posts by. |
time_frame | String | Optional timeframe of analytics to filter posts by. Default is "popular_past_year". Must be one of:"popular_all_time" "popular_past_year""popular_past_six_months" "popular_past_month"
This parameter is required when including the logical_operator parameter. |
logical_operator | String | When tag_slug contains multiple tags, use this operator to filter results with AND or OR logic. By default, this function uses OR logic to return posts tagged with any of the specified tags.When including this parameter, time_frame is required. |
blog_post_archive_url
The blog_post_archive_url function returns a full URL to the archive listing page for the given date values on the specified blog.
Please note:This function has a limit of 200 posts. This function also has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
href.
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_post_archive_url("default", 2017, 7, 5) }}">Posts from July 5th, 2017</a>
<a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/archive/2017/07/05"
>Posts from July 5th, 2017</a
>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use, either a specific blog by its ID or the default blog by "default". |
year | Integer | The year that the post was published. |
month | Integer | The month that the post was published. |
day | Integer | The day that the post was published. |
blog_recent_author_posts
The blog_recent_author_posts function returns a sequence of blog post objects for the specified author, sorted by most recent. This sequence of posts can be saved into a variable and iterated through with a for loop, creating a custom post listing of posts by a particular author.
The first line of the example below demonstrates how the function returns a sequence of posts by an author. In this example, rather than specifying an exact author name, the current post author is used. The sequence is saved in a variable and looped through. Any blog post variables should use the name of the individual loop item rather than content.. In the example, author_post.name is used. This technique can be used on blog and page templates.
Please note:This function has a limit of 200 posts and 10 calls per page and per email.
{{ blog_recent_author_posts("default", content.blog_post_author.slug, 5 ) }}
{% set author_posts = blog_recent_author_posts("default", content.blog_post_author.slug, 5) %}
{% for author_post in author_posts %}
<div class="post-title">{{ author_post.name }}</div>
{% endfor %}
[Post by author title 1, Post by author title 2, Post by author title 3, Post by
author title 4, Post by author title 5]
<div class="post-title">Post by author title 1</div>
<div class="post-title">Post by author title 2</div>
<div class="post-title">Post by author title 3</div>
<div class="post-title">Post by author title 4</div>
<div class="post-title">Post by author title 5</div>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to retrieve posts from. The blog ID is returned by the module blog field. |
author_slug | String | Specifies which author to filter posts by. This can be the content.blog_post_author.slug to use the author of the current post, or a lowercase hyphenated name such as "paul-bunyan". |
limit | Integer | Specifies the number of posts to add to the sequence up to a limit of 200. |
blog_recent_posts
The blog_recent_posts function returns a sequence of blog post objects for the specified blog, sorted by most recent first. This sequence of posts can be saved into a variable and iterated through with a for loop, creating a custom post listing of your most popular posts.
The function takes two parameters. The first parameter specifies which blog to collect popular posts from. The value should be "default" or the blog ID of a particular blog (available in the URL of the Blog dashboard). The second parameter specifies how many posts are retrieved.
The first line of the example below demonstrates how the function returns a sequence. The sequence is saved in a variable and looped through. Any blog post variables should use the name of the individual loop item rather than content.. In the example, rec_post.name is used. This technique can be used, not only on blog templates, but also regular pages.
Please note:This function has a limit of 200 posts and 10 calls per page and per email.
{{ blog_recent_posts("default", 5) }}
{% set rec_posts = blog_recent_posts("default", 5) %}
{% for rec_post in rec_posts %}
<div class="post-title">{{ rec_post.name }}</div>
{% endfor %}
[Recent post title 1, Recent post title 2, Recent post title 3, Recent post
title 4, Recent post title 5]
<div class="post-title">Recent post title 1</div>
<div class="post-title">Recent post title 2</div>
<div class="post-title">Recent post title 3</div>
<div class="post-title">Recent post title 4</div>
<div class="post-title">Recent post title 5</div>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use, either a specific blog by its ID or the default blog by "default". The blog ID is returned by the module blog field. |
limit | Integer | Specifies the number of posts to add to the sequence, maximum 200. |
blog_recent_tag_posts
The blog_recent_tag_posts function returns a sequence of blog post objects for a specified tag or tags, sorted by most recent first. This sequence of posts can be saved into a variable and iterated through with a for loop, creating a custom post listing of posts by a particular tag or tags.
In the example code below:
- The first line shows how the function returns a sequence of posts by tag.
- The second line shows how to save the function in a sequence variable. The rest of the code then uses a for loop to cycle through the variable values. Any blog post variables should use the name of the individual loop item rather than
content.. In the example, tag_post.name is used. You can use this technique on both blog and website pages.
Learn more about creating a related blog post listing.
Please note:This function has a limit of 100 posts and 10 calls per page and per email.
{{ blog_recent_tag_posts("default", "marketing-tips", 5) }}
{% set tag_posts = blog_recent_tag_posts("default", ["marketing", "fun", "inbound"], 3, "AND") %}
{% for tag_post in tag_posts %}
<div class="post-title">{{ tag_post.name }}</div>
{% endfor %}
[Post about Marketing 1, Post about Marketing 2, Post about Marketing 3, Post
about Marketing 4, Post about Marketing 5]
<div class="post-title">Post about Marketing</div>
<div class="post-title">Post about Fun</div>
<div class="post-title">Post about Inbound</div>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use, either a specific blog by its ID or the default blog by "default". The blog ID is returned by the module blog field. |
tag_slug | String | Specifies which tag to filter on. You can include up to 10 tags, comma separated. Tags with multiple words must be lowercase with spaces replaced by hyphens. |
limit | Integer | Specifies the number of posts to add to the sequence. This parameter is required when including a logical_operator. |
logical_operator | String | When tag_slug contains multiple tags, use this operator to filter results with AND or OR logic. By default, this function uses OR logic to return posts tagged with any of the specified tags.When including this parameter, limit is required. |
blog_tag_url
The blog_tag_url function returns a full URL to the specified blog tag’s listing page.
This function accepts two parameters. The first parameter specifies which blog the tag’s listing page exists in. The second parameter specifies which tag to link. This parameter can use the topic.slug for a particular tag from content.topic_list or accepts a lowercase hyphenated name such as "marketing-tips".
The example below shows how this function can be used as an anchor’s href.
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_tag_url("default", "inbound-marketing") }}">Inbound Marketing</a>
<a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/tag/inbound-marketing"
>Inbound Marketing</a
>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use, either a specific blog by its ID or the default blog by "default". |
tag_slug | String | Specifies which tag to link to. |
blog_tags
The blog_tags function returns a sequence of the 250 most blogged-about tags (based on number of associated blog posts) for the specified blog, sorted by blog post count.This sequence can be stored in a variable and iterated through to create custom tag post filters. The number of posts for each tag can be accessed with tag.live_posts.
This function accepts two parameters. The first parameter specifies which blog to fetch tags from. The second parameter sets a limit on the number of tags fetched.
The first line of the example below demonstrates how the function returns a sequence of tag objects. The rest of the example demonstrates a use case of saving a sequence into a variable and then iterating though the tag objects, printing a set of tag links. The example assumes that the blog has 4 tags.
Please note:This function has a limit of 250 tags.
{{ blog_tags("default", 250) }}
{% set my_tags = blog_tags("default", 250) %}
<ul>
{% for item in my_tags %}
<li>
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ blog_tag_url(group.id, item.slug) }}">{{ item }}</a>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
[ Blogging, Inbound Marketing, SEO, Social Media]
<ul>
<li><a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/tag/blogging">Blogging</a></li>
<li><a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/tag/inbound-marketing">Inbound Marketing</a></li>
<li><a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/tag/seo">SEO</a></li>
<li><a href="http://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/tag/social-media">Social Media</a></li>
</ul>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to use. The blog ID is returned by the module blog field. |
limit | Integer | The maximum amount of tags to return. |
blog_total_post_count
This function returns the total number of published posts in the specified blog. If no parameter is specified, it will count your default blog posts. Alternatively, you can specify "default" or a blog ID of a different blog to count. The blog ID is available in the URL of your blog dashboard for a particular blog.
Please note:This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
{{ blog_total_post_count }}
{{ blog_total_post_count(359485112) }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
selected_blog | Blog ID or “default” | Specifies which blog to count. The blog ID is returned by the module blog field. |
clear
Removes all items from a list. Unlike pop(), it does not return anything.
{% set words = ["phone","home"] %}
{% do words.clear() %}
{{words}}
color_contrast
This function validates color contrast based on WCAG standards. You’ll need to include two colors as arguments, and you can include an optional argument to specify the rating (AA or AAA). Returns true or false based on whether the colors meet/exceed the standard.
{{color_contrast('#FFFFFF','#273749')}}
{{color_contrast('rgb(255, 255, 255)','rgb(229, 237, 245)','AAA')}}
<p {% if color_contrast('rgb(12,31,1)', '#F0F', 'AA') %}style="color: #FF0000;"{% else %}style="color: #00FF00"{% endif %}>Hey there</p>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
color_1 | Color | The first color to compare. Accepts:- 6-digit hex codes (
#FFFFFF) - 3-digit hex codes (
#F0A) - RGB color codes (
rgb(12,31,1))
Can also use a variable that stores a hex or RGB color code. For example:theme.primary_color.color |
color_2 | Color | The second color to compare against the first. |
rating | String | The WCAG standard to use for rating. Can be either AA (default) or AAA. |
color_variant
This function lightens or darkens a hex value or color variable by a set amount. The first parameter is the hex color (for example (“#FFDDFF”) or a variable storing a hex value. The second parameter is the amount to adjust it by, from 0 to 255. This function can be used in CSS files to create a color variation. Another good use case is to use it with a color parameter of a color module, to allow users to specify a primary color that automatically generates a color variation.
In the example below, the hex color #3A539B is stored in a variable called base_color. The color is modified by -80 resulting in a darker blue (#00034B).
{% set base_color ="#3A539B" %}
{{ color_variant(base_color, -80) }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
base_color | HEX color string | The starting color to be altered. For example, #F7F7F7. |
brightness_offset | Integer | A positive or negative number used to lighten or darken the base color. |
content_by_id
Returns a landing page, website page or blog post by ID. The only parameter accepted by this function is a numeric content ID.
The below example code shows this function in use to generate a hyperlinked list item.
Please note:This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and 20 calls per email.
{% set my_content = content_by_id(4715624297) %}
<ul>
<li>
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ my_content.absolute_url }}">{{my_content.title}}</a>
</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li>
<a
href="http://www.hubspot.com/blog/articles/kcs_article/email/how-do-i-create-default-values-for-my-email-personalization-tokens"
>How do I create default values for my email or smart content
personalization tokens?</a
>
</li>
</ul>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
id | ID | The ID of the content to look up. |
content_by_ids
Given a list of content IDs, returns a dict of landing page, website page or blog posts matching those IDs.
This function takes one parameter, a list of page or blog post IDs to look up, placed within an array. Up to 100 content objects can be passed. The below example code shows this function in use to generate a list of hyperlinked list items.
Please note:This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
{% set contents = content_by_ids([4715624297, 4712623297, 5215624284]) %}
<ul>
{% for content in contents %}
<li>
<a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ content.absolute_url }}">{{content.title}}</a>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<ul>
<li>
<a
href="http://www.hubspot.com/blog/articles/kcs_article/email/how-do-i-create-default-values-for-my-email-personalization-tokens"
>How do I create default values for my email or smart content
personalization tokens?</a>
</li>
<li>
<a
href="https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/content-marketing-strategy-guide">Content Marketing Strategy: A Comprehensive Guide for Modern Marketers</a>
</li>
</ul>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
ids | List | A list of page or blog post IDs to look up. Up to 100 content objects can be passed. |
copy
Return a shallow copy of the list. Equivalent to a[:].
A shallow copy constructs a new compound object and then (to the extent possible) inserts references into it to the objects found in the original.
{% set a = ["ham"] %}
{% set b = a.copy() %}
a: {{a}}
b: {{b}}
After Append
{% do a.append("swiss") %}
a: {{a}}
b: {{b}}
a: [ham] b: [ham] After Append a: [ham, swiss] b: [ham]
count
Returns the number of times a variable exists in a list.
{% set attendees = ["Jack","Jon","Jerry","Jessica"] %}
{% set jon_count = attendees.count("Jon") %}
There are {{jon_count}} Jon's in the list.
<p>After append:</p>
{% do attendees.append("Jon") %}
{% set jon_count_after_append = attendees.count("Jon") %}
There are now {{jon_count_after_append}} Jon's in the list.
There are 1 Jon's in the list.
<p>After append:</p>
There are now 2 Jon's in the list.
crm_associations
Gets a list of CRM records associated with another record by its record ID, association category, and association definition ID.
Please note:
- For security purposes, of the HubSpot standard object types only the
product, and marketing_event objects can be retrieved on a publicly accessible page. Any other standard object type must be hosted on a page which is either password protected or requires a membership login. Custom objects do not have this same restriction.
- This function can be called a maximum of 10 times per page and per email. Each
crm_associations call can return at most 100 objects. The default limit is 10 objects.
{% set associated_contacts = crm_associations(847943847, "HUBSPOT_DEFINED", 2, "limit=3&years_at_company__gt=2&orderBy=email", "firstname,email", false) %}
{{ associated_contacts }}
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|
id | ID | ID of the record to find associations from. |
association category | String | The category of the association definition. Possible values are HUBSPOT_DEFINED, USER_DEFINED, and INTEGRATOR_DEFINED. This parameter can be omitted for hubspot defined built-in association types. |
association type id | Integer | The ID of the association definition to use. For standard HubSpot supported objects see ID of the association type to use.Otherwise, this association ID can found at the CRM Objects Schema API. |
query | String | The id of the record OR a query string, delimited by &. All expressions are ANDed together. Supported operators are:eq (default)neqltltegtgteis_nullnot_nullinnincontains (applicable for multi-valued properties or string properties, e.g., “firstname__contains=Tim”)
Queries can include the following parameters:limit: the maximum number of results returned in the response. For example, limit=50.offset: for paging through the results if the number of returned results is higher than the limit parameter. For example, offset=51.orderBy: order results by a specific property. For example, orderBy=email.
|
properties | String | Optional. A comma-separated list of properties to return. By default, a small set of common properties are returned. The ID property is always returned.A full list of properties can be found using the get all contact properties and get all company properties endpoints. |
formatting | Boolean | Optional. Format values such as dates and currency according to the account’s settings. Omit or pass false for raw strings. |
{has_more=true, offset=3, total=203, results=[{firstname=Aimee, id=905,
email=abanks@company.com}, {firstname=Amy, id=1056, email=abroma@company.com},
{firstname=Abigael, id=957, email=adonahu@company.com}]}
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|
has_more | Boolean | Indicates there are more results available beyond this batch (total > offset). |
total | Integer | The total number of results available. |
offset | Integer | The offset to use for the next batch of results. |
results | Array | The associated objects matching the function’s parameters. |
crm_object
Gets a single CRM record by query or by its ID. Records are returned as a dict of properties and values.
This function can also be used with custom and integrator objects.
Please note:
- For security purposes, of the HubSpot standard object types only the
product, and marketing_event objects can be retrieved on a publicly accessible page. Any other standard object type must be hosted on a page which is either password protected or requires a membership login. Custom objects do not have this same restriction.
- This function can only be called a maximum of 10 times on a single page.
<!-- by query -->
{% set contact = crm_object("contact", "email=contact@company.com", "firstname,lastname", false) %}
<!-- by id -->
{% set contact = crm_object("contact", 123) %}
{{ contact.firstname }}
{{ contact.lastname }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
object_type | String | The object type name. Object type names are case sensitive. The supported object types. To find the names of the account specific and integrator object types available in your account use the CRM Objects Schema API to get the type definitions and look for the name property. It contains the internal object type name that should be used in the function. For integrator and account specific object types with the same name as the built-in objects use the objects fully qualified name (FQN). |
query | String | Optional. The id of the record OR a query string, delimited by &. All expressions are ANDed together. Supported operators are:eq (default)neqltltegtgteis_nullnot_nullinnincontains (applicable for multi-valued properties or string properties, e.g., "firstname__contains=Tim").
Queries can include the following parameters:limit: the maximum number of results returned in the response. For example, limit=50.offset: for paging through the results if the number of returned results is higher than the limit parameter. For example, offset=51.orderBy: order results by a specific property. For example, orderBy=email.
|
properties | String | Optional. A comma-separated list of properties to return. By default, a small set of common properties are returned. The ID property is always returned.A full list of properties can be found using the get all contact properties and get all company properties endpoints. |
formatting | Boolean | Optional. Format values such as dates and currency according to the account’s settings. Pass false for raw strings. |
Please note:When building a query, the values of range, distinct, ndistinct, and startswith are reserved keywords. To query a property that uses one of those names, you’ll need to use the following format: range__eq= (rather than range=).
crm_objects
Gets a list of records for a specific object type from the HubSpot CRM.
Please note:
- For security purposes, of the HubSpot standard object types only the
product, and marketing_event objects can be retrieved on a publicly accessible page. Any other standard object type must be hosted on a page which is either password protected or requires a membership login. Custom objects do not have this same restriction.
- This function can be called a maximum of 10 times per page and per email. Each
crm_objects call can return at most 100 objects. The default limit is 10 objects.
crm_objects("contact", "firstname=Bob&order=lastname&order=createdate") will order contacts with the first name "Bob" by last name and then by createdate. To reverse a sort, prepend - to the property name (e.g., order=-createdate). The CRM objects function can also be used with custom and integrator objects.
{% set objects = crm_objects("contact", "firstname__not_null=&limit=3", "firstname,lastname") %}
{{ objects }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
object_type | String | The object type name (case-sensitive). See supported object types. For custom objects, you’ll need to use the Fully Qualified Name (FQN), which can be found using the Schemas API. |
query | String | The ID of the record or a query string, delimited by &. All expressions are ANDed together. Supported operators are:eq (default)neqltltegtgteis_nullnot_nullinnincontains (applicable for multi-valued properties or string properties, e.g., "firstname__contains=Tim").
Example: "email=contact@company.com" |
properties | String | A comma-separated list of properties to return. By default, a small set of common properties are returned. You can retrieve all properties for an object using the Properties API. |
formatting | Boolean | Format values such as dates and currency according to the account’s settings. Pass false for raw strings. |
{has_more=true, offset=3, total=331, results=[{firstname=Brian, id=44151,
lastname=Halligan}, {firstname=Dharmesh, id=44051, lastname=Shah},
{firstname=George, id=88551, lastname=Washington}]}
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|
has_more | Boolean | Indicates there are more results available beyond this batch (total > offset). |
total | Integer | The total number of results available. |
offset | Integer | The offset to use for the next batch of results. |
results | Array | The associated objects matching the function’s parameters. See results properties below for more information. |
Please note:When building a query, the values of range, distinct, ndistinct, and startswith are reserved keywords. To query a property that uses one of those names, you’ll need to use the following format: range__eq= (rather than range=).
crm_property_definition
Get the property definition for a given object type and property name.
Supported object types are HubSpot standard objects (e.g., contacts), account-specific objects, and integrator objects.
{% set prop = crm_property_definition("contact", "firstname") %}
{{ prop.label }}
{{ prop.type }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
object_type | String | The object type name (case-sensitive). See supported object types. For custom objects, you’ll need to use the Fully Qualified Name (FQN), which can be found using the Schemas API. |
property_name | String | The case-insensitive property name to retrieve the definition for. |
crm_property_definitions
Get the property definitions for a given object type and set of property names.
Supported object types are HubSpot standard objects (e.g. contacts), account-specific objects, and integrator objects.
{% set props = crm_property_definitions("contact", "firstname,lastname") %}
{{ props.firstname.label }}
{{ props.lastname.label }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
object_type | String | The object type name (case-sensitive). See supported object types. For custom objects, you’ll need to use the Fully Qualified Name (FQN), which can be found using the Schemas API. |
property_name | String | Optional. The case-insensitive property names comma separated, to retrieve the definition for. If empty, the definitions for all the properties will be retrieved. |
cta
Because CTA modules have so many parameters that contain variations of their code, you can use the CTA function to easily generate a particular CTA in a template, page, or email. This function is what the rich text editor uses when you add a CTA via the editor.
Please note:This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
{{ cta("ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b") }}
{{ cta("ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b", "justifycenter") }}
<span
class="hs-cta-wrapper"
id="hs-cta-wrapper-ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b"
>
<span
class="hs-cta-node hs-cta-ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b"
id="hs-cta-ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b"
style="visibility: visible;"
>
<a
id="cta_button_158015_19a9097a-8dff-4181-b8f7-955a47f29826"
class="cta_button "
href="//cta-service-cms2.hubspot.com/ctas/v2/public/cs/c/?cta_guid=19a9097a-8dff-4181-b8f7-955a47f29826&placement_guid=ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b&portal_id=158015&redirect_url=APefjpH34lXcq1H4FhyHhE3DNeHPNigbBluiv6t07-N80GLkyj2Dn9PizhW8bo4ecrS47RmyslLg7QQKWLG7n2oNkvrumL9dWUjMMEjVYvStZ-IMyulMBvdU8AddI6nFXL0G_VPP_VXmnFi66RKPPjPvx6kbyPO6k566noP4CTZMyADHkGsGBf4S95YdTNtTTFabShT62cVAiV_oWlXbpfPWQc4G3IvkoDoAhmpQVW-ggUcKa4Ft_5A&hsutk=683eeb5b499fdfdf469646f0014603b4&utm_referrer=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.davidjosephhunt.com%2F%3Fhs_preview%3DNVkCLfFf-2857453560&canon=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.davidjosephhunt.com%2F-temporary-slug-63bb220d-eda6-44d0-9738-af928e787237"
style=""
cta_dest_link="http://www.hubspot.com/free-trial"
title="Start a HubSpot trial"
>
Start a HubSpot trial
</a>
</span>
<script charset="utf-8" src="//js.hscta.net/cta/current.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
hbspt.cta.load(158015, 'ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b');
</script>
</span>
<span
class="hs-cta-wrapper"
id="hs-cta-wrapper-ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b"
>
<span
class="hs-cta-node hs-cta-ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b"
id="hs-cta-ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b"
style="display: block; text-align: center; visibility: visible;"
>
<a
id="cta_button_158015_19a9097a-8dff-4181-b8f7-955a47f29826"
class="cta_button "
href="//cta-service-cms2.hubspot.com/ctas/v2/public/cs/c/?cta_guid=19a9097a-8dff-4181-b8f7-955a47f29826&placement_guid=ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b&portal_id=158015&redirect_url=APefjpH34lXcq1H4FhyHhE3DNeHPNigbBluiv6t07-N80GLkyj2Dn9PizhW8bo4ecrS47RmyslLg7QQKWLG7n2oNkvrumL9dWUjMMEjVYvStZ-IMyulMBvdU8AddI6nFXL0G_VPP_VXmnFi66RKPPjPvx6kbyPO6k566noP4CTZMyADHkGsGBf4S95YdTNtTTFabShT62cVAiV_oWlXbpfPWQc4G3IvkoDoAhmpQVW-ggUcKa4Ft_5A&hsutk=683eeb5b499fdfdf469646f0014603b4&utm_referrer=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.davidjosephhunt.com%2F%3Fhs_preview%3DNVkCLfFf-2857453560&canon=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.davidjosephhunt.com%2F-temporary-slug-63bb220d-eda6-44d0-9738-af928e787237"
style=""
cta_dest_link="http://www.hubspot.com/free-trial"
title="Start a HubSpot trial"
>
Start a HubSpot trial
</a>
</span>
<script charset="utf-8" src="//js.hscta.net/cta/current.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
hbspt.cta.load(158015, 'ccd39b7c-ae18-4c4e-98ee-547069bfbc5b');
</script>
</span>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
guid | String | The ID of the CTA to render. Can be found in the URL of the details screen of the CTA. |
align_opt | Enumeration | Adjusts alignment of CTA. Values include justifyleft, justifycenter, justifyright, justifyfull. |
extend
Extend a list by appending all items from an iterable. In other words, insert all list items from one list into another list.
{% set vehicles = ["boat","car","bicycle"] %}
{% set more_vehicles = ["airplane","motorcycle"] %}
{% do vehicles.extend(more_vehicles) %}
{{vehicles}}
[boat, car, bicycle, airplane, motorcycle]
file_by_id
This function returns the metadata of a file by ID. It accepts a single parameter, the numeric ID of the file to look up. To retrieve multiple files at once, use the files_by_ids function instead.
Please note:This function is limited to 10 calls per page and per email.
{% set file = file_by_id(123) %}
{{ file.friendlyUrl }}
https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/HubSpot_Logos/HSLogo_color.svg
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
file_id | Number | The ID of the file to look up. |
files_by_ids
Returns the metadata of multiple files by ID. It accepts an array of file IDs.
Please note:This function limited to 10 calls per page and per email, and can accept up to 100 file IDs.
{% set files = files_by_ids([123,456])%}
{% for file in files %}
URL:{{file.friendlyUrl}}
<br>
{% endfor %}
URL:https://api-na1.hubspot.com/filemanager/api/v2/files/123/example-file-1
URL:https://api-na1.hubspot.com/filemanager/api/v2/files/456/example-file-2
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
file_id | Number | The IDs of the files to look up, separated by commas (up to 100). |
{% set objects = crm_objects("contact", "email=bh@hubspot.com", "file").results %}
{% for item in objects %}
<!-- Need to use split filter as CRM property returns a string that is semi-colon separated -->
{% set fileIDs = item.file|split(";") %}
{% set files = files_by_ids(fileIDs) %}
{% for file in files %}
<div>
File name: {{file.name}}
<br>
Friendly Url: {{file.friendlyUrl }}
<br>
Url: {{file.url }}
<hr><br>
</div>
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
flag_content_for_access_check
When a blog post is configured for self-registration access, visitors will need to register or log in to view the full post content. HubSpot’s default blog listing assets automatically include this functionality, and will also include a lock icon indicator for posts that require self-registration to access. Learn more about building custom solutions using this function and its corresponding API.
This function checks whether a blog post can be accessed by the current visitor. When called, the function is replaced with the following attribute:
hs-member-content-access=<true/false>
A value of true indicates that the blog post requires the visitor to log in to view the full content.
{% for content in contents %}
<article {{ flag_content_for_access_check(content.id) }} >
...
</article>
{% endfor %}
<article hs-member-content-access="true">...</article>
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
ID | ID | The ID of the content that will be checked against the current logged in viewer. |
follow_me_links
Returns the social media account links set in account settings. Used in the default follow_me module.
{% set fm = follow_me_links() %}
{{ fm }}
[FollowMeLink{type=URL, id=5142734, altName=RSS,
followMeUrl=http://website.com/rss.xml, iconName=rss,
name=http://website.com/rss.xml}]
{{ format_address('en-us', { address: "25 First Street", address2: "2nd Floor", city: "Cambridge", state: "MA", country: "United States", zip: "02141"}) }}
[25 First Street, 2nd Floor, Cambridge, MA 02141, United States]
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
locale | String | The locale to format the address in. |
address | String | The street address. |
address2 | String | The second line of the address, such as floor or apartment number. |
city | String | The city of the address. |
state | String | The state of the address. |
country | String | The country of the address. |
zip | String | The zip code of the address. |
{{ format_company_name("companyName", addJapaneseHonorifics) }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
companyName | String | The name of the company. |
useHonorificIfApplicable | Boolean | When set to true and the context’s language is Japanese, a Japanese company honorific will be added where appropriate. |
{{ format_name("firstName", "surname", addJapaneseHonorifics) }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
firstName | String | The person’s first name. |
surname | String | The person’s surname or last name. |
useHonorificIfApplicable | Boolean | When set to true and the context’s language is Japanese, a Japanese honorific will be added where appropriate. Default is false. |
datetimeformat function.
{{ format_datetime(content.publish_date, "short", "America/New_York", "en") }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
format | String | The format to use. Can be one of: |
timeZone | String | The time zone of the output date in IANA TZDB format. |
locale | String | The locale to use for locale-aware formats. |
geo_distance
This function contains 4 parameters and calculates the ellipsoidal 2D distance between two points on Earth. Use this function as a filter query for getting HubDB data.
{% for row in hubdb_table_rows(1234567, "geo_distance(loc,1.233,-5.678,mi)__gt=500") %}
{{row.name}} <br>
{% endfor %}
Cambridge, MA<br />
Salem, MA<br />
San Diego, CA<br />
Chicago, IL<br />
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
point1 | Location | location from a HubDB column. |
point2_lat | Latitude | Latitude of point2. |
point2_long | Longitude | Longitude of point2. |
units | String | Units for the return value. Options are FT for feet, MI for miles, M for meters or KM for kilometers. |
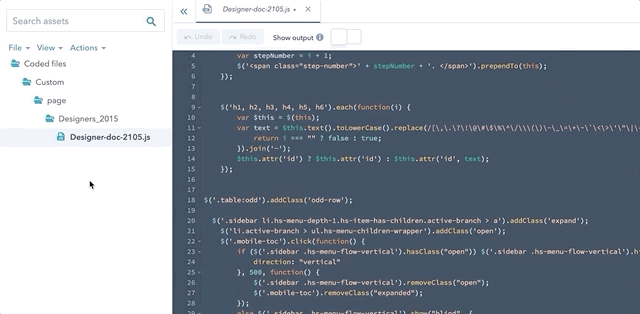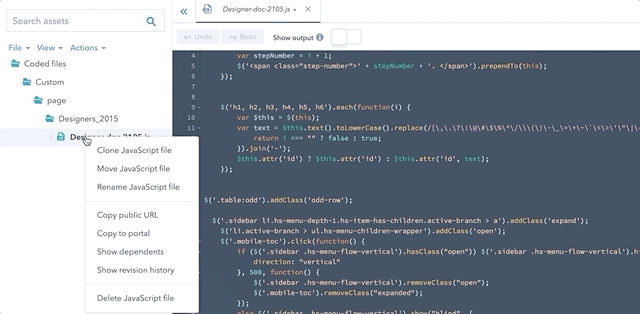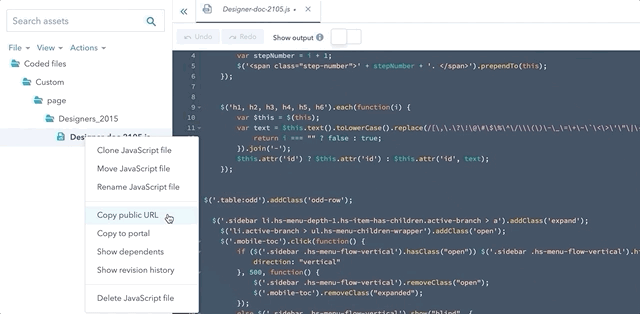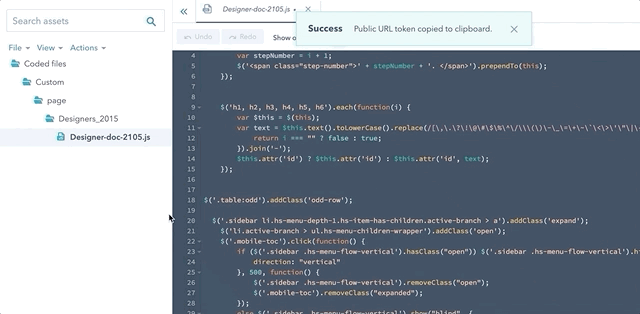
get_asset_url
This function returns the public URL of a specified template or code file. The parameter of this function is the asset’s path in the design manager. Coded file URLs update each time you publish them; therefore, by using this function your ensure you are always using the latest version of the file.
You can automatically generate this function in the app, by either right-clicking a file and selecting Copy public URL, or by clicking Actions, then selecting Copy public URL.
The example below gets the URL of a Javascript file authored in Design Manager that can be included as the src of a <script> tag.
{{ get_asset_url("/custom/styles/style.css") }}
//cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/1234567/hub_generated/template_assets/1565970767575/custom/styles/style.min.css
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
path | String | The design manager file path to the template or file. |
get_public_template_url_by_id
This function works just like get_public_template_url, returning public URL of a specified template or code file. The only difference is the parameter of this function is the template ID (available in the URL of the template or coded file), instead of the design manager path.
{{ get_public_template_url_by_id("2778457004") }}
//cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/327485/hub_generated/style_manager/1431479563436/custom/page/Designers_2015/designer-doc-2105.min.js
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
template_id | ID | The ID number of the template of file. |
hubdb_table
Please note:
- HubDB requires Content Hub Professional or Enterprise.
- This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
hubdb_table function can be used to get metadata from a HubDB table, specified by table ID. You can access the follow metadata attributes via dot notation:
name: the name of the table.columns: a list of column information.created_at: the timestamp of when this table was first created.published_at: the timestamp of when this table was published.updated_at: timestamp of when this table was last updated.row_count: the number of rows in the table.
{% set table_info = hubdb_table(1548215) %}
{{ table_info.row_count }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
table_id | String | ID or name of the table. |
hubdb_table_column
Please note: HubDB requires Content Hub Professional or Enterprise. HS_ID and hs_id are both valid.
The following metadata is available:
name: the name of the column.label: the label to be used for the column.type: the type of the column.options: for columns of type select, a map of optionId to option information.foreignIds: for columns of type foreignId, a list of foreignIds (with id and name properties).
In addition to the above attributes, you can also use getOptionByName("<option name>") for select type columns. This method retrieves information for the specified option.
{% set column_info = hubdb_table_column(123456, 6) %}
{{ column_info.label }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
table_id | String | ID or name of the table. |
column | String | ID or name of the column (case insensitive). |
hubdb_table_row
Please note:
- HubDB requires Content Hub Professional or Enterprise.
- This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
hubdb_table_row function can be used to pull a single row from a HubDB table. From a row, you can pull information from each table cell by calling on the corresponding attribute:
hs_id: the globally unique id for this row.hs_created_at: a timestamp representing when this row was created.hs_path: when used with dynamic pages, this string is the last segment of the url’s path for the page.hs_name: when used with dynamic pages, this is the title of the page.<column name> or ["<column name>"]: get the value of a column for this row, specified by the name of the column. Column names are not case sensitive. For example, HS_ID and hs_id are both valid.
{% set row = hubdb_table_row(1548264, 6726439331) %}
{{ row.role }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
table_id | String | ID or name of the table. |
row_id | Integer | ID of the row of the table. |
hubdb_table_rows
Please note:
- HubDB requires Content Hub Professional or Enterprise.
- This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
- If you use a random filter on this function, the page will be prerendered periodically. This means that the filtered content will not be updated on every page reload.
hubdb_table_rows function can be used to query rows of a HubDB table, which can be useful for iterating through row values.
By default, this function will return a maximum of 1,000 rows. To retrieve more rows, specify a limit in the query, as shown in the code below.
{% for row in hubdb_table_rows(1546258, "years_at_company__gt=3&orderBy=count&limit=1500") %}
the value for row {{ row.hs_id }} is {{ row.name }}
{% endfor %}
the value for row 6726439331 is Brian Halligan the value for row 8438997836 is
Dharmesh Shah
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
table_id | String | ID or name of the table to query. |
query | String | A query in the same format as a URL query string. If not passed, returns all rows. Learn more about the available filters for querying HubDB table rows.
You can sort the returned rows by including the orderBy parameter and specifying a column. To reverse the sort, prepend the column name with -. Learn more about sorting HubDB rows. |
Please note:When building a query, the values of range, distinct, ndistinct, and startswith are reserved keywords. To query a property that uses one of those names, you’ll need to use the following format: range__eq= (rather than range=).
include_default_custom_css
This function generates a link tag that references the Primary CSS file (default_custom_style.min.css). This file is designed to be a global CSS file that can be added to all templates. To render, the function requires a boolean parameter value of True.
{{ include_default_custom_css(True) }}
<link
href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs//cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/327485/hub_generated/style_manager/1420345777097/custom/styles/default/hs_default_custom_style.min.css"
rel="stylesheet"
/>
index
Returns a number representing the location of the first matching item in a 0-based array.
This function accepts 3 parameters:
- The item in the array that you want to find (required)
- The starting index of the slice of the array to search
- The ending index of the slice of the array to search
{% set shapes = ["triangle","square","trapezoid","triangle"] %}
triangle index: {{shapes.index("triangle")}}
<br>
trapezoid index: {{shapes.index("trapezoid")}}
<hr>
Adjusted start and end:
<br>
triangle index: {{shapes.index("triangle",1,5)}}
triangle index: 0
trapezoid index: 2
<hr />
Adjusted start and end:
triangle index: 3
insert
Places an element into a list at the specific index provided.
This function accepts two parameters:
- Index: the position where an element is to be inserted.
- Element: the item to be inserted.
{% set even_numbers = [2,4,8,10] %}
{% do even_numbers.insert(2,6) %}
{{even_numbers}}
locale_name
Returns a human-readable string representation of a language code, optionally translated to a target language.
{{ locale_name("es") }}
{{ locale_name("es", "en") }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
language_code | String | The language code. |
target_language_code | String | The language that the output will be translated to. |
load_translations
Loads translations from a given _locales folder path and returns a map of the values.
Learn more about including field translations in custom modules and themes.
{% set template_translations = load_translations('../_locales', 'fr', 'en') %}
{{ partial_footer_address }}
123 Rue du Pont, Ville, Région, 12300
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
path | String | The file path to the _locales directory of the translations. |
language_code | String | The language code. |
language_code_fallback | String | The language code fallback if the specified language_code isn’t present. |
null to the menu function it will return an empty pylist. You can also specify a menu by name. In most cases it’s safer to use the menu id, as a menu being renamed won’t affect the id. If building for the marketplace it makes sense to default to "default" if menu is null.
Please note:This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
{% set node = menu(987) %}
{% for child in node.children %}
{{ child.label }}<br>
{% endfor %}
{% set default_node = menu("default") %}
{% for child in default_node.children %}
{{ child.label }}<br>
{% endfor %}
page1<br />
page2<br />
page3<br />
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
menu_id | Id | Required. The id of the menu passed as a number. |
root_type | Enumeration | Root type of the menu ("site_root", "top_parent", "parent", "page_name", "page_id", "breadcrumb")."site_root" denotes static - Always show top-level pages in menu."top_parent" denotes dynamic by section - Show pages in menu that are related to section being viewed."parent" denotes dynamic by page - Show pages in menu that are related to page being viewed."breadcrumb" denotes breadcrumb style path menu (uses horizontal flow).
|
root_key | String | Root key (id or name) when using "page_name" or "page_id". |
module_asset_url
Gets the URL for an asset attached to a custom module via Linked Files > Other Files.
{{ module_asset_url("smile.jpg") }}
https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/6178146/logo-black-color.png
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
name | String | The name of the asset. |
namespace
Creates a namespace object that can hold arbitrary attributes. It can be initialized from a dictionary or with keyword arguments.
{% set ns = namespace({"name": "item name", "price":"100"}, b=false) %}
{{ns.name}}, {{ns.b}}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
dictionary | Map | The dictionary to initialize with. |
kwargs | String | Keyword arguments to put into the namespace dictionary. |
oembed
Returns OEmbed data dictionary for given request. Only works in emails.
{{ oembed({ url: "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KqpFNtbEOh8"}) }}
OEmbedResponse{type=video, version=1.0, html=<iframe
width="480"
height="270"
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/KqpFNtbEOh8?feature=oembed"
frameborder="0"
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture"
allowfullscreen
></iframe
>, title=Marketing Is a Marathon — Build a Complete Customer Experience,
authorName=HubSpot, authorUrl=https://www.youtube.com/user/HubSpot,
providerName=YouTube, providerUrl=https://www.youtube.com/,
thumbnailUrl=https://i.ytimg.com/vi/KqpFNtbEOh8/hqdefault.jpg,
thumbnailWidth=480, thumbnailHeight=360}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
request | String | Request object, {url: string, max_width: long, max_height: long}. |
personalization_token
Returns the value of a contact or contact related property, or a default.
Hi {{ personalization_token("contact.firstname", "there") }}!
<!-- If the contact is known -->
Hi Dharmesh!
<!-- If the contact is unknown -->
Hi there!
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
expression | String | An expression for the object and property to render. |
default | String | Optional. A default value to use if the expression has no value. |
pop
Removes the item at the index from the list. Also returns the removed item if printed.
{% set even_numbers = [2,3,4,6,8,9,10] %}
{% do even_numbers.pop(1) %}
{{even_numbers.pop(4)}}
{{even_numbers}}
postal_location
The postal_location function returns the latitude/longitude location pair for a given postal code and country code (limited to US, CA, and GB).
{{ postal_location("02139") }}
{% set location = postal_location("02139", "US") %}
{{ location.latitude }}
{{ location.longitude }}
LatLon{latitude=42.3647, longitude=-71.1042} 42.3647 -71.1042
Please note:This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
postal_code | String | Postal code of the location. |
country_code | String | Country code for the postal code. If not provided, the country will try to be inferred from the postal code. |
put
Similar to the update function, which updates a dict with the elements from another dict object or from an iterable of key-value pairs, except that put supports variable names in dicts.
{% set dict_var = {"authorName": "Tim Robinson"} %}
{% set key = "key" %}
{% set value = "value" %}
{% do dict_var.put(key, value) %}
{{ dict_var }}
{authorName=Tim Robinson, key=value}
range
Returns a list containing an arithmetic progression of integers. With one parameter, range will return a list from 0 up to (but not including) the value. With two parameters, the range will start at the first value and increment by 1 up to (but not including) the second value. The third parameter specifies the step increment. All values can be negative. Impossible ranges will return an empty list. Ranges can generate a maximum of 1000 values.
Range can be used within a for loop to specify the number of iterations that should run.
{{ range(11) }}
{{ range(5, 11) }}
{{ range(0, 11, 2) }}
{% for number in range(11) %}
{{ number }}
{% endfor %}
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] [5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] [0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10] 0 1 2
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
require_css
This function enqueues a CSS file to be rendered in the head element. All CSS link tags are grouped together and render before any JavaScript tags. The HubL is replaced with an empty line and then a link tag is added to {{ standard_header_includes }}. This method requires an absolute URL; CMS content with a known relative URL can be required by using the get_asset_url() function.
To enqueue an inline style to be rendered in the head via a style tag element, use the {% require_css %} and {% end_require_css %} tag instead with your style tags and CSS inside of that.
The second parameter is a dictionary of options to modify generated tag. Supports async (true/false) a technique described on web.dev and any other key-value pair will be added as HTML attributes to the style tag.
{{ standard_header_includes }}
<!-- more html -->
{{ require_css("http://example.com/path/to/file.css") }}
{{ require_css(get_asset_url("/relative/path/to/file.css")) }}
<!-- you can tell the browser to load the file asynchronously -->
{{ require_css(get_asset_url("./style.css"), { async: true }) }}
<!-- other standard header html -->
<link
type="text/css"
rel="stylesheet"
href="http://example.com/path/to/file.css"
/>
<link
type="text/css"
rel="stylesheet"
href="http://example.com/relative/path/to/file.css"
/>
<!-- you can tell the browser to load the file asynchronously -->
<link
rel="preload"
href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs//cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/6333443/hub_generated/template_assets/39079350918/1608661506628/example.css"
as="style"
onload="this.onload=null;this.rel='stylesheet'"
/>
<noscript
><link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs//cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/6333443/hub_generated/template_assets/39079350918/1608661506628/example.css"
/></noscript>
<!-- more html -->
require_js
Specifies whether a script should be enqueued to render in the head or footer (default). Specify the render location by including the head or footer parameter. The HubL will be replaced by an empty line, and included in either the header or footer includes.
To enqueue an inline script to be rendered in the footer via a script element, wrap your <script> tags with {% require_js %} and {% end_require_js %}.
You can also include additional render options in this function. These will be added as HTML attributes in the script tag. Render options include:
- position:
head/footer
- defer:
true/false
- async:
true/false
- type:
string
{{ standard_header_includes }}
<!-- more html -->
{{ require_js("http://example.com/path/to/footer-file.js", "footer") }}
{{ require_js("http://example.com/path/to/head-file.js", "head") }}
<!-- you can add async or defer attributes to the tags that are added. -->
{{ require_js(get_asset_url("./path/to/file.js"), { position: "footer", async: true }) }}
{{ require_js(get_asset_url("./jquery-latest.js"), { position: "footer", defer:true }) }}
{{ standard_footer_includes }}
<!-- other standard header html -->
<script
async
defer
src="//cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/6333443/hub_generated/template_assets/37785718838/1605816776975/jquery-latest.min.js"
></script>
<script src="http://example.com/path/to/head-file.js"></script>
<!-- more html -->
<script src="http://example.com/path/to/footer-file.js"></script>
<!-- you can add async or defer attributes to the tags that are added. -->
<script
async
src="//cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/######/hub_generated/template_assets/#############/######/jquery-latest.min.js"
></script>
<script
defer
src="//cdn2.hubspot.net/hub/######/hub_generated/template_assets/#############/######/jquery-latest.min.js"
></script>
<!-- other standard footer html -->
resize_image_url
Rewrites the URL of image stored in File Manager to a URL that will resize the image on request. The function accepts one required parameter, and five optional parameters. At least one optional parameter must be passed.
Please note:Images that are larger than 4096 pixels in height or width will not be automatically resized. Instead, you’ll need to manually resize the image. {{ resize_image_url("http://your.hubspot.site/hubfs/img.jpg", 0, 0, 300) }}
http://your.hubspot.site/hubfs/img.jpg?length=300&name=img.jpg
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
url | String | URL of a HubSpot-hosted image. |
width | Integer (px) | The new image width, in pixels. |
height | Integer (px) | The new image height, in pixels. |
length | Integer (px) | The new length of the largest side, in pixels. |
upscale | Boolean | Use the resized image dimensions even if they would scale up the original image (images may appear blurry).Default value is false. |
upsize | Boolean | Return the resized image even if it is larger than the original in bytes.Default value is false. |
reverse
Reverses the order of items in a list. Doesn’t take any parameters. To reverse an object or return an iterator to iterate over the list in reverse, use |reverse
{% set numbers = [1,2,3,4] %}
{% do numbers.reverse() %}
{{numbers}}
super
This function prints content from the parent template into a child template using the extends tag.
For example, in the code below, a basic HTML template has been created with a HubL block named sidebar and saved as parent.html. A second template file is created that will extend that parent file. Normally, the <h3> would be printed in the parent HTML’s sidebar block. But by using super, content from the parent template sidebar block is combined with the content from the child template.
{% extends "custom/page/web_page_basic/parent.html" %}
{% block sidebar %}
<h3>Table Of Contents</h3>
{{ super() }}
{% endblock %}
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>This is the parent template</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Table of contents</h3>
Sidebar content from parent.
</body>
</html>
today
Returns the start of today (12:00am). Optionally you can add a parameter to change the timezone from the default UTC.
{{ today() }}
{{ today("America/New_York") }}
{{ unixtimestamp(today("America/New_York").plusDays(1)) }}
2018-10-23T00:00Z 2018-10-23T00:00-04:00[America/New_York] 1540353600000
to_local_time
Converts a UNIX timestamp to the local time, based on your HubSpot Report Settings. You can then apply a datetimeformat filter to format the date.
{{ to_local_time(eastern_dt) }}
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
date | Datetime | UNIX timestamp to convert to local time. |
topic_cluster_by_content_id
Returns a HubL dict representing the topic cluster associated with a piece of content (determined by the passed content id), including metadata about the associated pillar page, core topic, and subtopics. Can be used to “auto-link” a piece of content with its associated pillar page [if it exists].
Available metadata can be found in: attachableContent (the current content’s metadata), topic (the current content’s associated topic metadata), coreTopic (the associated cluster’s core topic metadata), and pillarPage (the associated pillar page’s metadata).
Use {{ topicCluster|pprint }} to see a full a display of available properties/attributes.
{{ topic_cluster_by_content_id(content.id) }}
{%- if content.id -%}
{%- set topicCluster = topic_cluster_by_content_id(content.id) -%}
{%- if topicCluster.pillarPage.url.value and topicCluster.pillarPage.publishState == "PUBLISHED" -%}
<div>Topic: <a href="https://developers.hubspot.com/docs{{ topicCluster.pillarPage.url.value }}">{{ topicCluster.coreTopic.phrase }}</a></div>
{%- endif -%}
{%- endif -%}
{ attachedContent, topic, coreTopic, pillarPage } (AttachedContentWithContext:
{attachedContent=AttachedContent{id=1234, topicId=1234, clusterId=1234,
portalId=0, attachable=Attachable{contentId=124,
url=ValidatedUri{https://www.hubspot.com/}, attachableType=LANDING_PAGE,
title=title, publishState=PUBLISHED, deletedAt=null}, isLinkedToPillarPage=null,
isPillarPage=null, createdAt=1547238986475, updatedAt=1547238986475,
deletedAt=null}, coreTopic=Optional[Topic{id=1234, portalId=0, clusterId=1234,
phrase=TOPIC PHRASE, attachedContent=null, isCoreTopic=false,
createdAt=1547157062081, updatedAt=1547232313421, deletedAt=null}],
pillarPage=Optional[AttachedContent{id=1234, topicId=1234, clusterId=1234,
portalId=0, attachable=Attachable{contentId=null,
url=ValidatedUri{https://www.hubspot.com.com/}, attachableType=EXTERNAL_URL,
title=null, publishState=PUBLISHED, deletedAt=null}, isLinkedToPillarPage=null,
isPillarPage=null, createdAt=1547157062086, updatedAt=1547157062086,
deletedAt=null}], topic=Optional[Topic{id=1234, portalId=0, clusterId=8345,
phrase=topic phrase, attachedContent=null, isCoreTopic=false,
createdAt=1547238962703, updatedAt=1547238962703, deletedAt=null}]})
<div>Topic: <a href="#-link-to-pillar-page-url"> core topic phrase </a></div>
Please note:This function has a limit of 10 calls per page and per email.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
content_id | Id | The id of the page to look up. |
truncate
The truncate function works just like the truncate filter, but uses function syntax instead of filter syntax. The first parameter specifies the string. The second parameter specifies the length at which to truncate. The final parameter specifies the characters to add when the truncation occurs.
Please note:Because this function relies on the spaces between words to shorten strings, it may not work as expected for languages without spaces between characters, such as Japanese.
{{ truncate("string to truncate at a certain length", 19, false, "...") }}
{% set longString = "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Phasellus sodales ultricies velit sit amet ornare." %}
{{ truncate(longString, 40, false, "...") }}
string to truncate ... Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur ...
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|
string_to_truncate | String | String that will be truncated. |
length | integer | Specifies the length at which to truncate the text (includes HTML characters). |
killwords | boolean | If true, the string will cut text at length, regardless of if it’s in the middle of a word. |
end | String | The characters that will be added to indicate where the text was truncated. |
type
This function accepts one argument and returns the type of an object. The return value is one of: "bool", "datetime", "dict", "float", "int", "list", "long", "null", "str" or "tuple".
{{ type("Blog") }}
{% set my_type = type("Blog") %}
<p>{{my_type}}</p>
unixtimestamp
This function returns a unix timestamp when you supply a datetime object.
update
Updates the dict with the elements from another dict object or from an iterable of key-value pairs. Use this function to combine or merge objects.
{% set dict_var = {"authorName": "Douglas Judy", "authorTitle": "Mastermind" } %}
{% do dict_var.update({"authorFriend": "Jake"}) %}
{% do dict_var.update({"authorLocation": "unknown"}) %}
{{ dict_var }}
{authorName=Douglas Judy, authorTitle=Mastermind, authorFriend=Jake,
authorLocation=unknown}