Basic module syntax
You can include a module in a template file using{% %} statement delimiters, followed by specifying either module or dnd_module, depending on the implementation. dnd_module denotes a module within a drag and drop area. Then, configure the module using a set of module detail fields, listed below. These fields can be formatted as individual lines or as a single block.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
"unique_module_name" | String | A custom name to identity the module, which should be unique within the context of the template. This name is used for populating the module with content added through the page editor. The name must be in quotes, and must be the second value defined within the module (after module/dnd_module).If a page contains multiple modules with the same name, content added through the page/email editor will appear in both module instances. |
path | String | The path of the module, either the path found in design manager or a relative path when developing locally. HubSpot default module paths always start with @hubspot/. |
| Additional parameters | String | Boolean | Integer | Enumeration | JSON object | Additional parameters to configure the module’s behavior and how it renders.
|
Passing dicts to module parameters
For modules with fields that expect dicts, you can pass them like you would other parameters. If it’s cleaner to you or you plan to re-use the values, you can set the dict to a variable, and pass the variable to the parameter instead.Passing fields that have dnd associated parameters
Drag and drop tags, such asdnd_area, come with a set of default parameters, such as width. While the design manager will prevent you from creating new fields that use one of these reserved parameters, modules created before drag and drop tags were introduced may already use a reserved parameter.
To fix this, you can use the fields parameter. Just like you would pass field data to a group, you can pass the field name as a key on the fields object. Its value must be consistent with the format the field type expects.
Setting default field values in templates
You can set default values for module fields at the template level by including parameters in thednd_module tags. Below, learn how to set default field values in nested field groups, repeating fields, repeating field groups, and style fields.
Nested field groups
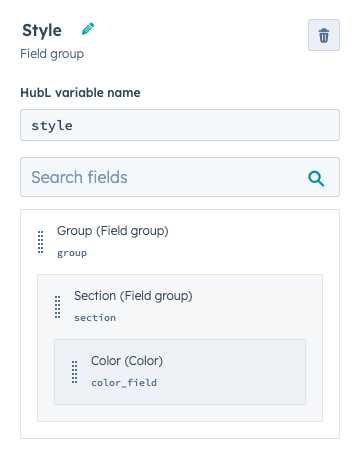
Below is an example of a custom drag and drop module with a customstyle field group containing other nested field groups. Compare its template-level configuration with how this same grouping would appear in the design manager.
Repeating fields
You can set template-level default values for repeating fields by passing an array to the field’s parameter. The array’s items must be in the format expected based on the field type. For example:- A simple text field only expects a string
- An image repeater field expects an image field object. This applies to all of the other field types.
Repeating field groups
Modules that contain repeating groups of fields, like you might see in a slideshow module or FAQ module, can have a template-level default set for those groups. To do this, pass an array of objects to your field group’s parameter. The key-value pairs of the object are the field names and their values.Style fields
you can explicitly set default values for style fields using thestyles parameter.
This works just like other groups do, where the parameter is the name of the group. You pass an object to that parameter with all of the fields you wish to set.
Block syntax
While most modules have parameters that control default content, there may be situations where you need to add large code blocks to the default content of a module. For example, you may want to include a large block of HTML as the default content for a rich text or HTML module. Rather than trying to write that code into a value parameter, insert the module using a{% module_block %} tag, then include within it a {% module_attribute %} tag that specifies content by the name of the field.
As an example, the following code would insert a custom <p> element into the html field of a default rich text module instance.
widget_block, widget_attribute, and type_of_module parameters. These parameters have been replaced by {% module_block %}/{% module_attribute %}. Learn more by expanding the section below.
content_attribute
In addition to regular and block syntax, there are certain instances where you may want to specify a large block default content for a predefined content variable. The most common example of this proves to be the content.email_body variable. This variable prints a standard email body that can be altered in the content editor. Since this isn’t a standard HubL module, we use a content_attribute tag to specify a block of default content. The example below shows the email body variable populated with a default content code block.Parameters available for all modules
While some modules have certain special parameters, below is a list of parameters supported by all modules.| Parameter | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
label | String | The name of the module displayed in the content editor. This parameter can also be used to give users additional instructions. | |
overrideable | Boolean | Controls whether or not the module can be edited in the content editor, equivalent to the Prevent editing in content editors setting in the design manager. | True |
no_wrapper | Boolean | When set to True, removes the wrapping markup from around the content of a module.On pages, modules are always wrapped in a <div> with special classes. This wrapping markup makes it so when you click the module in the preview pane, the editor scrolls to that module. There may be instances where you want to remove the wrapper, such as if you want to use a text module to populate the destination of an anchor tag href attribute. | False |
extra_classes | String | Adds classes to the module wrapper. You can add multiple classes by separating the classes with spaces. For example:extra_classes='full-width panel' | |
export_to_template_context | Boolean | When set to True, instead of rendering the HTML, the parameters from this widget will be available in the template context. Learn how to use this parameter and the widget_data tag. | False |
unique_in_loop | Boolean | When the module is defined within a loop, appends the module name with the loop.index. When set to True, a different version of the module will print within each iteration of the loop. Appends the module name with the loop.index. | False |
Field-based parameters
When defining a module in a template file, you can pass additional parameters to the module based on the module’s defined fields. For HubSpot default modules, you can find available parameters in the default web modules reference. When working with modules locally, you can find a module’s fields in thefields.json file.
The format for the parameter value depends on the field’s type. For example, the default button module includes a link field, which accepts a JSON object. In the template, you could pass those URL details as shown below.
link_field instead of link, your module code would need to include a link_field parameter instead.
| Field | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Blog | Integer (blog ID) | 1234567890 |
| Boolean | True/False | False |
| Choice | String | "option_1" |
| Color | Object | See color parameters |
| CTA | String (CTA ID) | "fb9c0055-6beb-489d-8dda-3e1222458750" |
| Date | Integer (timestamp) | 1566360000000 |
| Datetime | Integer (timestamp) | 1566360000000 |
| Email address | Array of email address strings | ["develop@hubspot.com", "design@hubspot.com"] |
| File | String (URL of file) | "https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/file.pdf" |
| Follow Up Email | Integer (follow up email ID) | 1234567890 |
| Font | Object | See font parameters |
| Form | Object | See form parameters |
| HubDB Table | Integer (HubDB table ID) | 123456789 |
| Icon | Object | See icon parameters |
| Image | Object | See image parameters |
| Link | Object | See link parameters |
| Logo | Object | See logo parameters |
| Meeting | String (meeting link) | "https://app.hubspot.com/meetings/developers-r-kewl" |
| Menu | Integer (menu ID) | 123456789 |
| Number | Integer | 1 |
| Page | Integer (page ID) | 1234567890 |
| richtext | String (can contain HTML) | "# Hello, world!" |
| Salesforce Campaign | String (Salesforce campaign ID) | "7016A0000005S0tQAE" |
| Simple Menu | Array of menu item objects | See simple menu parameters |
| Tag | Integer (tag ID) | 1234567890 |
| Text | String | "string it together" |
| URL | Object | See URL parameters |
Color parameters
Pass a color field parameter as a JSON object containing a hexadecimal color code and numerical opacity value.Font parameters
Pass a font field parameter as a JSON object containing font configuration details.Form parameters
Pass a form field parameter as a JSON object containing form configuration details| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
form_id | String | The form’s ID. Learn how to find a form ID in HubSpot. |
response_type | String | The behavior after form submission. Can be one of:
|
redirect_url | String | The redirect URL (if redirecting) |
redirect_id | String | The ID of a HubSpot page to redirect to (if redirecting) |
message | String | The message to display after submission (if displaying an inline text message). |
Icon parameters
Pass an icon field parameter as a JSON object containing FontAwesome icon configuration details.| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | String | The icon’s name. |
unicode | String | The icon’s unicode value. |
type | String | The type of icon. Can be one of: "SOLID", "REGULAR" |
redirect_id | String | The ID of a HubSpot page to redirect to (if redirecting) |
message | String | The message to display after submission (if displaying an inline text message). |
Image parameters
Pass an image field parameter as a JSON object containing image configuration details.Link parameters
Pass a link field parameter as a JSON object containing link configuration details. Learn more about url types in the link field reference.Logo parameters
Pass a logo field parameter as a JSON object containing logo configuration details.Simple menu parameters
Pass a simple menu parameter as an array containing JSON objects of menu configuration details. You can link either to pages that are hosted in the HubSpot account, or external pages by URL.| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
isPublished | Boolean | Whether the page is published (for HubSpot-hosted pages). |
pageLinkId | Integer | The page ID (for HubSpot-hosted pages). |
pageLinkName | Boolean | The page’s name (for HubSpot-hosted pages). |
isDeleted | Boolean | Whether the page has been deleted (for HubSpot-hosted pages). |
categoryId | Integer | The ID of the page category. Can be one of:
|
subCategory | String | The page subcategory. Can be one of: site_page, landing_page, blog, normal_blog_post. |
contentType | Integer | The page’s content type. Can be one of: site_page,landing_page,blog |
state | String | The publish state of the page. Can be one of:
|
linkLabel | String | The text that will be displayed for the menu item. |
linkUrl | String | The URL of the menu item. |
linkParams | String | Query parameters appended to the link URL (for menu items of the PAGE_LINK_WITH_PARAMS type). |
linkTarget | String | Set to "_blank" to open the link in a new browser tab. |
type | String | The type of menu item. Can be one of:
|
children | Array | An array of sub-menu items. |
URL parameters
Pass a URL field parameter as a JSON object containing logo configuration details. Similar to link field parameters, but with fewer customization options.| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
type | String | The type of link. Can be one of:
|
href | String | The URL of the link. |
content_id | String | The ID of the page you’re linking to (for HubSpot-hosted pages). |