- Access account, extension, and user context
- Perform actions like displaying alert banners
- Log custom messages for debugging
- Render the UI through UI components
Registering the extension
UI extensions, like any React front-end, are written as React components. However, unlike typical React components, you must register your UI extension with HubSpot by includinghubspot.extend() inside the component file instead of exporting it. This is not required when you create a sub-component. For cleaner code, reuse and include them inside your extension.
The hubspot.extend() function receives the following arguments:
context: provides account, extension, and user context to the extension.actions: makes actions available to the extension.
hubspot.extend() or the extension component.
Access context data
Thecontext object contains data related to the authenticated user and HubSpot account, along with data about where the extension was loaded. You can access context data using either approach:
- Props-based approach: destructure
contextfrom the callback passed tohubspot.extend(), then pass it to your component as a prop. - Hook-based approach: call the
useExtensionContexthook directly within your component.
context object has the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
location | 'crm.record.tab' | 'crm.record.sidebar' | 'crm.preview' | 'helpdesk.sidebar' | 'settings' | 'home' | The UI extension’s location. |
portal.id | Number | The ID of the HubSpot account. |
portal.timezone | String | The account’s timezone. |
portal.dataHostingLocation | 'na1' | 'na2' | 'na3' | 'ap1' | 'eu1' | Geographic identifier that denotes the region where the current portal is hosted. See HubSpot Cloud Infrastructure FAQ for more details. |
user.id | Number | The user’s ID. |
user.email | String | The user’s primary email address. |
user.emails | Array | All of the user’s associated email addresses. |
user.firstName | String | The user’s first name. |
user.lastName | String | The user’s last name. |
user.locale | String | The user’s locale. |
user.teams | Array | An array containing information about teams that the user is assigned to. Each team object contains the id and name of the team, along with a teammates array that lists the IDs of other users on the team. |
user.permissions | Array | An array of permission strings (e.g., 'integrations-management-write'). |
variables | Object | All of the project’s config profile variables. |
crm.record.tab, crm.record.sidebar, crm.preview, helpdesk.sidebar):
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
crm.objectId | Number | The ID of the CRM record (e.g., contact ID). |
crm.objectTypeId | String | The ID of the CRM record’s object type (e.g., 0-1). See the full list of object IDs for reference. |
extension.appId | Number | The extension’s app ID. |
extension.appName | String | The name of the extension’s app. |
extension.cardTitle | String | The extension’s title. |
Actions
Below are the actions you can perform with the SDK. You can access actions using either a props-based approach or a hook-based approach:- Props-based approach: destructure
actionsfrom the callback passed tohubspot.extend(), then pass it to your component as a prop. - Hook-based approach: call the
useExtensionActionshook directly within your component.
Note that some UI components include a set of actions separate from the SDK actions below, such as the CRM action components.
Universal actionsSupported in all extension points:
settings, home, crm.record.tab, crm.record.sidebar, crm.preview, helpdesk.sidebar| Action | Description |
|---|---|
addAlert | Display alert banners to the user. |
reloadPage | Reload the current page. |
copyTextToClipboard | Copy text to the user’s clipboard. |
closeOverlay | Close an open overlay or modal. |
openIframeModal | Open an iframe in a modal window. |
CRM property actionsOnly available in
crm.record.tab, crm.record.sidebar, crm.preview, helpdesk.sidebar| Action | Description |
|---|---|
fetchCrmObjectProperties | Fetch property values from the current CRM record. |
refreshObjectProperties | Refresh CRM record properties on the page. |
onCrmPropertiesUpdate | Listen for updates to CRM record properties. |
Display alert banners
Use theaddAlert method to send alert banners as a feedback for any actions to indicate success or failure. addAlert is a part of the actions object that can be passed to extension via hubspot.extend. If you instead want to render an alert within a card, check out the Alert component.
.png) For example, the code below results in an app card that displays a success alert after fetching data from an external source. Note that the
For example, the code below results in an app card that displays a success alert after fetching data from an external source. Note that the addAlert action is passed into hubspot.extend() and the Extension component, then is triggered when the hubspot.fetch() function successfully executes.
| Prop | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
title | String | The bolded text of the alert. |
message | String | The main alert text. |
type | 'info' (default) | 'tip' | 'success' | 'warning' | 'danger' | The color of the alert.
|
Fetch CRM property data
There are multiple ways to fetch CRM property data via the SDK:- The
useCrmPropertieshook, which fetches properties from the current CRM record. While similar tofetchCrmObjectProperties, it offers automatic state management, supports property formatting, and automatically updates as properties are changed without needing to refresh. - The
fetchCrmObjectPropertiesaction, which fetches property data client-side at extension load time. This method is described below. propertiesToSend, which can be included in yourhubspot.fetch()functions to fetch property data on the back-end at function invocation time.- Use GraphQL to query CRM data through the
/collector/graphqlendpoint. Learn more about querying CRM data using GraphQL.
fetchCrmObjectProperties method, you can get property values from the currently displaying CRM record without having to use HubSpot’s APIs. This method is a part of the actions object that can be passed to the extension via hubspot.extend. You’ll first need to add the object to objectTypes inside the card’s .json config file. The objects you specify in objectTypes will also set which CRM objects will display the extension.
fetchCrmObjectProperties is formatted as:
Refresh properties on the CRM record
UserefreshObjectProperties to refresh the property data on the CRM record, and any CRM data components on the record without needing to refresh the page. This includes cards added to the record through HubSpot’s UI. This method will work for the CRM objects that you include in the extension’s .json file in the objectTypes array.
Listen for property updates
UseonCrmPropertiesUpdate to subscribe to changes made to properties on the CRM record and run hubspot.fetch() functions based on those changes. This only includes changes made from within the HubSpot UI, not property updates from outside the UI, such as via APIs. This action is intended to be used like a React hook.
The full API for this method is as follows:
error argument to the callback.
Open overlays
To add another layer of UI to your extension, you can include overlays using the Modal and Panel components.Modal: a pop-up dialog box best suited for short messages and action confirmations. A'danger'variant is included for destructive actions, such as deleting a contact.Panel: a slide-out sidebar best suited for longer, compartmentalized tasks that users might need to perform, such as multi-step forms. Includes a'modal'variant to obscure page content outside of the panel to focus the user on the panel task.
- Add the
overlayprop to a Button, LoadingButton, Link, Tag, or Image component. - Add the
ModalorPanelcomponent into theoverlayprop.
- Panel
- Modal
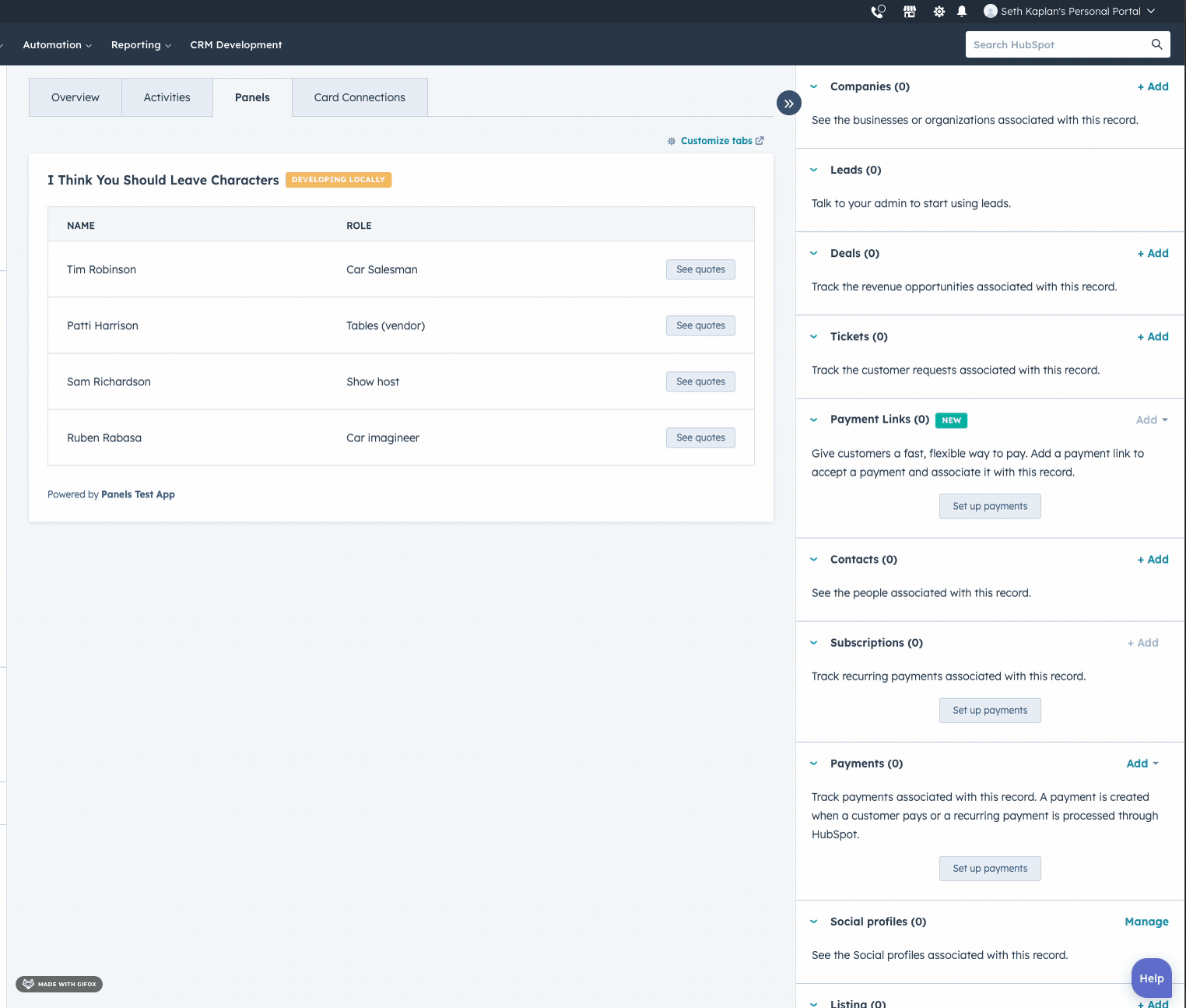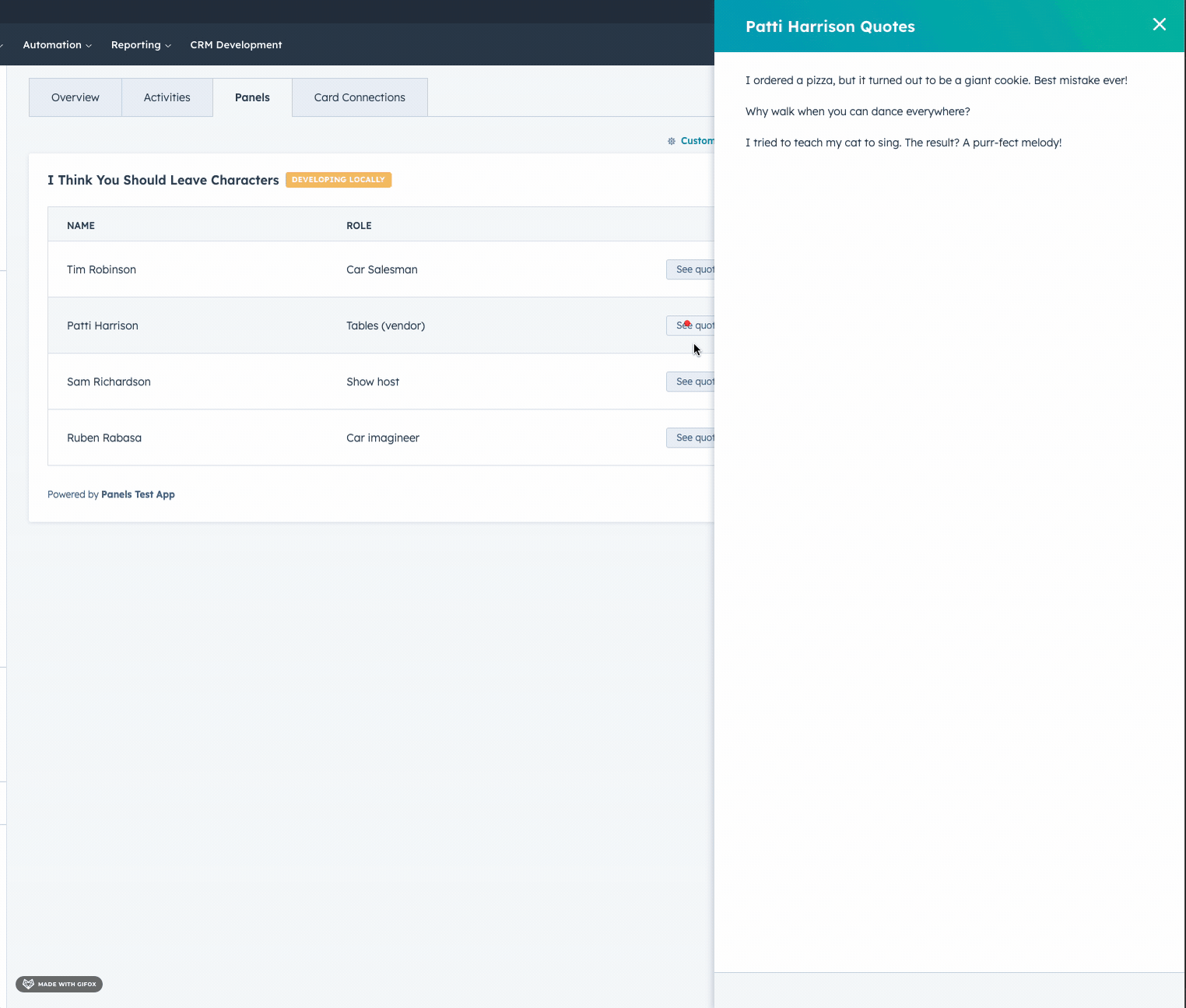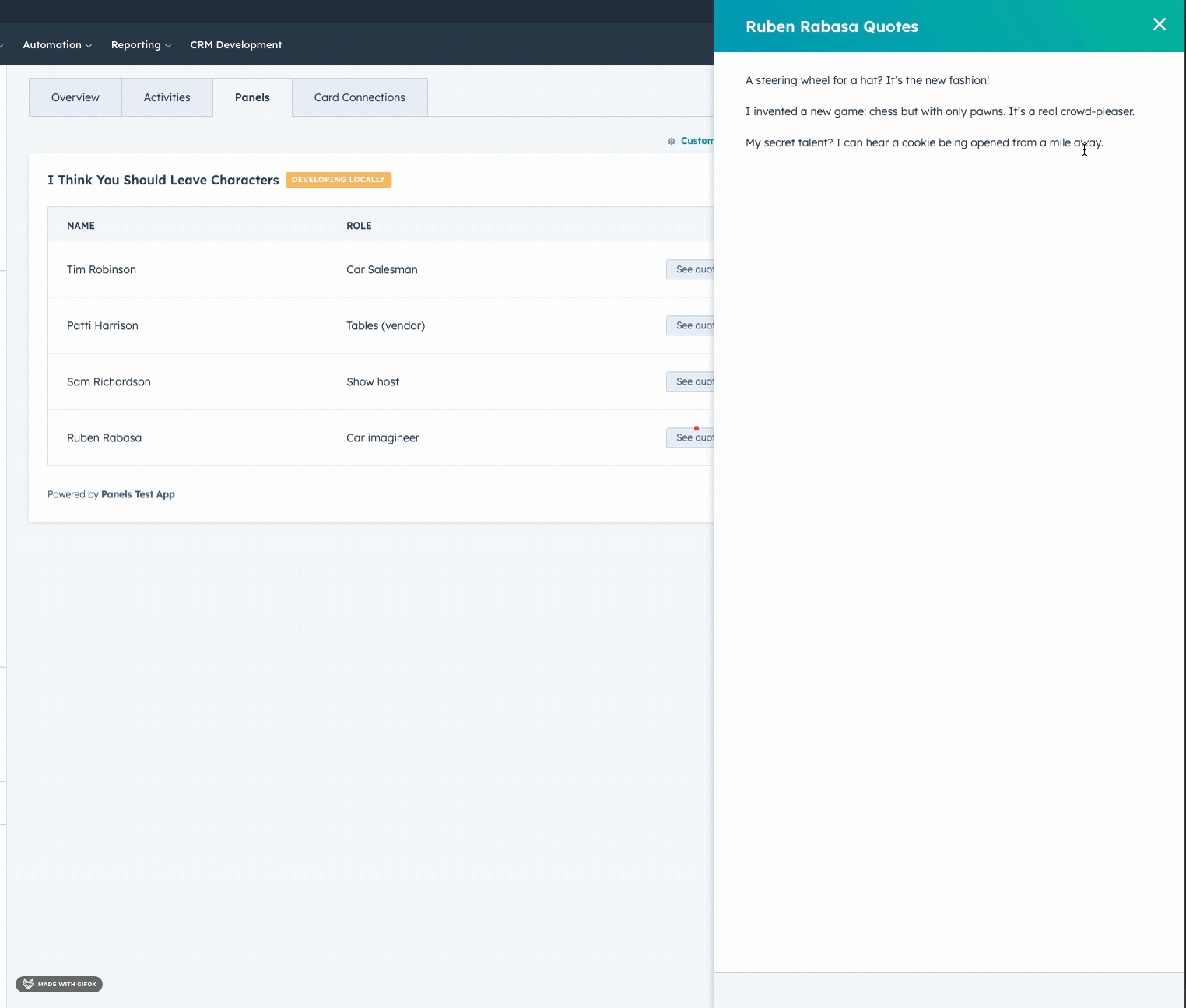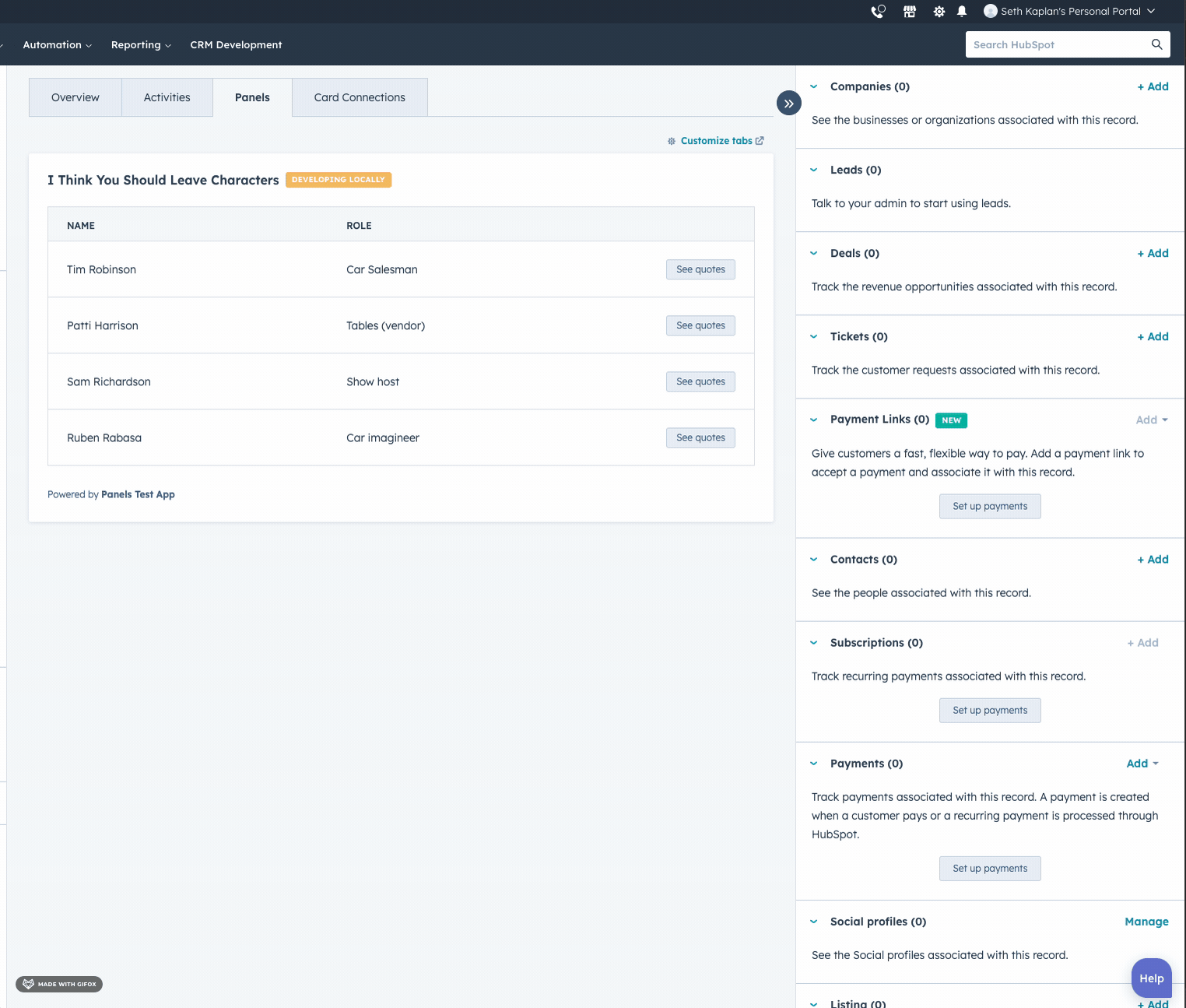

Open an iframe in a modal
Use theopenIframeModal action to open an iframe in a modal window. This action accepts a payload object and an optional callback function that runs when the modal is closed.
The payload object for openIframeModal includes the following fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
uri | String | The URL to load in the iframe. |
height | Number | The height of the modal in pixels. |
width | Number | The width of the modal in pixels. |
title | String | The title displayed at the top of the modal. |
flush | Boolean | When true, removes the default padding around the iframe content. |
onClose | Function | A callback function that runs when the modal is closed. Does not receive any parameters. |
window.postMessage to signal that the user is done. The following messages are accepted:
{"action": "DONE"}: the user has successfully completed the action.{"action": "CANCEL"}: the user has canceled the action.
uri you passed into the openIframeModal action. If the domains do not match, the message will be ignored.
Copy text to clipboard
Use thecopyTextToClipboard action to copy text to your clipboard. This action can be accessed through the actions argument (actions.copyTextToClipboard) and returns a promise that resolves once the system clipboard has been updated. Its functionality is provided by the Clipboard: writeText() method and follows the same requirements.
This action only works after the user has interacted with the page after loading (transient activation).
Reload page
Use thereloadPage action to reload the current page. This action can be accessed through the actions argument (actions.reloadPage).
Upload files
While there is no UI component for uploading files, there are a few ways you can upload files:- Create a custom file type property, then use a CRM property list component to display and manage the property from CRM records. You can upload up to 10 files per file property, and file uploaded via file properties have the same size and type limitations as files uploaded to the file manager.
- Include an iframe modal in the extension that loads an upload page, then upload files through the iframe.
Hooks
The SDK provides hooks to simplify accessing context, performing actions, and fetching CRM data within UI extensions. These hooks are optimized to prevent unnecessary re-renders and automatically clean up resources when components unmount. You can pass inline arrays and objects to the hooks directly, as memoization is not required.Universal hooks
These hooks are available in all extension points (crm.record.tab, crm.record.sidebar, crm.preview, helpdesk.sidebar, settings, and home).
useExtensionApi: access both context and actions from a single hook.useExtensionContext: access contextual information about the extension environment.useExtensionActions: access actions that can be performed within HubSpot.
useExtensionApi
TheuseExtensionApi hook provides access to available actions and contextual information from a single hook, for extension components that need access to both actions and context.
Otherwise, it’s best practice to use the more specific useExtensionActions or useExtensionContext, depending on your use case.
- For a complete list of available context properties, see Access context data.
- For a complete list of available actions, see Actions. The actions available depend on the extension point location.
useExtensionApi hook to display an alert (action) containing the user’s first name (context) when a button is clicked.
- Basic usage
- Typed usage
useExtensionContext
TheuseExtensionContext hook provides access to contextual information about the current extension environment, including location and other relevant data.
For a complete list of available context properties, see Access context data.
The following example accesses the current extension location and renders it in a Text component:
- Basic usage
- Typed usage
useExtensionActions
TheuseExtensionActions hook provides access to various actions that can be performed within the HubSpot interface. It’s a generic hook that can be typed with specific extension point locations for better TypeScript support.
For a complete list of available actions, see Actions. The actions available depend on the extension point location.
The following example displays an alert when a button is clicked:
- Basic usage
- Typed usage
CRM-specific hooks
These hooks are only available in CRM extension points (crm.record.tab, crm.record.sidebar, crm.preview, and helpdesk.sidebar).
useCrmProperties: fetch properties from the current CRM recorduseAssociations: fetch associated CRM records
useCrmProperties
TheuseCrmProperties hook fetches properties from the current CRM record with optional formatting. It accepts an array of properties to fetch, along with an optional object to format the returned data.
- Call
- Response
- Example usage
Either
'all' or an array of property names to format.Contains formatting options for the values returned from date, datetime, and currency properties.
- The
dateanddateTimeobjects can includeformatandrelativesubfields:format(string): a date or datetime string likeMM-DD-YYYYorMM-DD-YYYY:mm:ss. Supports standard date time string formats.relative(boolean): set totrueto display the amount of time passed since the returned value (e.g.,(1 day ago)or(1 hour ago)).
- The
currencyobject can includeaddSymbol(boolean), which sets whether the currency symbol should display with the number. Set totrueto display the currency symbol.
useAssociations
TheuseAssociations hook fetches CRM records of a specific object type associated with the currently displaying record. It accepts an object containing configuration details for the association fetch request, and an optional object that formats returned property data.
- Call
- Response
- Example usage
Configures the association data fetch request with:
toObjectType: the object type ID to fetch associations from (e.g., ‘0-1’ for contacts).properties: an optional array of properties to fetch from associated records.pageLength: an optional number of items per page (defaults to 10).
Either
'all' or an array of property names to format.Contains formatting options for the values returned from date, datetime, and currency properties.
- The
dateanddateTimeobjects can includeformatandrelativesubfields:format(string): a date or datetime string likeMM-DD-YYYYorMM-DD-YYYY:mm:ss. Supports standard date time string formats.relative(boolean): set totrueto display the amount of time passed since the returned value (e.g.,(1 day ago)or(1 hour ago)).
- The
currencyobject can includeaddSymbol(boolean), which sets whether the currency symbol should display with the number. Set totrueto display the currency symbol.
Best practices
Always use TypeScript generics
Extract hook calls to component level
Send custom log messages for debugging
Usinglogger methods, you can send custom log messages to HubSpot for more in-depth troubleshooting of deployed extensions. Custom log messages will appear in the app’s logs in HubSpot.
The following methods are available:
logger.infologger.debuglogger.warnlogger.error

Notes and limitations
- Custom log messages are not sent while in local development mode. They are logged to the browser console instead.
- All logs are sent as batches with a maximum of 100 logs per batch.
- Each HubSpot account is rate limited to 1,000 logs per minute. After exceeding that limit, all logging is stopped until the page is reloaded.
- The logger will queue a maximum of 10,000 pending messages. Any subsequent logs will be dropped until the queue is below the maximum.
- Queued logs are processed at a rate of five seconds per log batch.
- Queued logs are dropped when the page or is refreshed or closed.
.gif)